The male nude in art is not as often talked about as its female counterpart. However, apart from being easy on the eye, the male body in art is full of history and has undergone a host of fascinating transformations over the past 2000 years. We’ve put together 9 key moments for a tour of historical art. Read on, and we’ll reveal all.
1) The God
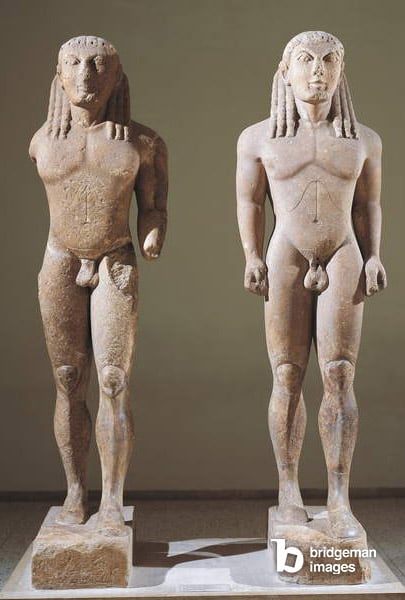

Our first stop on this quick tour is Ancient Greece. Spanning several centuries, the art of the Ancient Greeks is hard to summarise, but it certainly shows an increasing tendency towards lifelikeness. You only have to look at the difference between 7th Century BC kouroi (or “youths”), with their long hair and static bodies and statues from the classical period (5thC BC), with their athletic physique and relaxed pose (characterised by a little hip swing), called contrapposto.

The Greeks imagined their gods to look like perfect humans, and so the images of these deities have an idealising quality that carried through to other subjects too. The idealising nature of the male nude in this period runs even deeper, as physical beauty was often associated with goodness (in Plato’s philosophy for example). Lastly, it has also been suggested that the statues’ chiselled abs may be more than just eye candy: being a militant people, the Greeks represented soldier-like male bodies, with muscular structures that resembled armour.
2) The Sinner
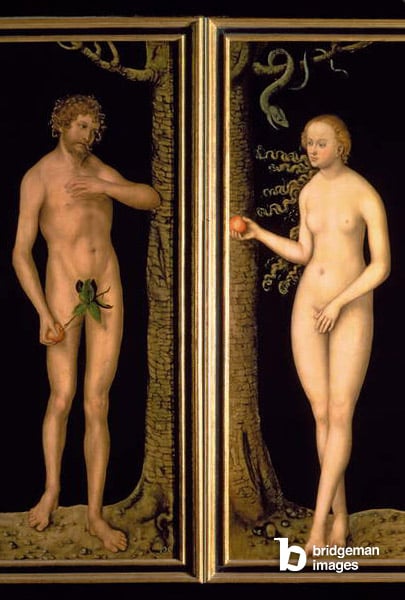

In the Middle ages, the male nude flips 180 degrees: from the proud, in-your-face nakedness of Antiquity, nudity becomes awkward. Not only does the naked statue become a symbol of Antiquity’s pagan religion (which didn’t go down well in the Bible-dominated culture of this period) and there was no need for similar imagery in Christianity, but nudity itself gets a more complicated position.
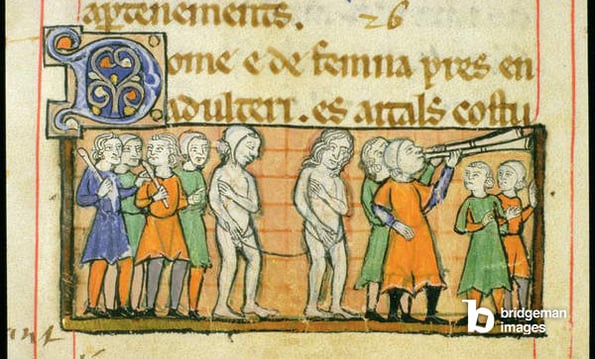
Associated with Original Sin and questions of (im)morality, nudity almost turns into something to be embarrassed about. This is reflected in painted, drawn and sculpted bodies, which become slight and slender, without the same emphasis on naturalism.
3) The Renaissance Man

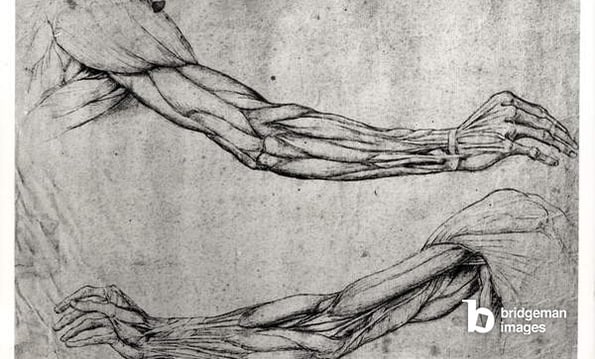
The naturalism of the Renaissance nude is however not just informed by the Ancient tradition, but shows a bigger shift in thinking: instead of seeing life on earth as a mere prologue to a nice afterlife (like in the Middle Ages), life on earth and therefore “being human” was valued much more. The school of thought associated with this is called “humanism”, and the realism of the nude in the Renaissance shows this new importance and appreciation of the human body.
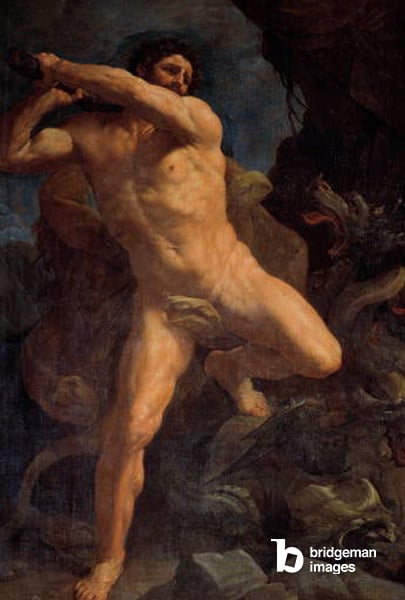

With a renewed interest in naturalism in the arts, the nude also becomes a site for an artist to show his skills: with its various textures, depths and shadows, the body became a great artistic test. To achieve the ultimate naturalism, artists became increasingly involved with anatomical study too.
4) Pushed to Extremities

Over the course of the sixteenth and early seventeenth-centuries something peculiar happens: artists start pushing the male body, far beyond the naturalistic, balanced physique of earlier Renaissance art. Muscles start to bulge and torsos and limbs are twisted in impossible positions. Michelangelo’s Battle of Cascina (only known to us through copies after the lost original) is the ultimate example of this more extreme, bodybuilder-type male body.

5) Following the Rules

The establishment of Art Academies across Europe from the sixteenth through to the eighteenth century (including the Royal Academies of Art in France and England) had a big impact on the male nude. Not only did these academies bring along a very regulated, classicised style, but life drawing was seen as a central element of artistic education, so yet again an eye for realistic bodily structure was valued. Furthermore, as the Academies favoured grand classical and historical subjects, the male nude often pops up as a strong, masculine, heroic character.

6) Masculinity Questioned

From the late 18th and during the course of the 19th century, the way the male body looks is no longer a given. In France for example, after the Napoleonic wars had shown a less heroic side of conflict and had changed the look of the male population (a lot of which was now scarred or missing limbs), artists experiment with a different type of male body, including a body that is not overtly masculine, such as Girodet’s Endymion. Towards the end of the nineteenth-century this still perseveres (consider for example the medieval-inspired, boyish males of Pre-Raphaelite art in England), but this time also sees the emergence of strongly realistic portrayals of men by artists such as Courbet and Millet. The ideal view of masculinity taught at the academies makes way for real people.
7) Changed Man
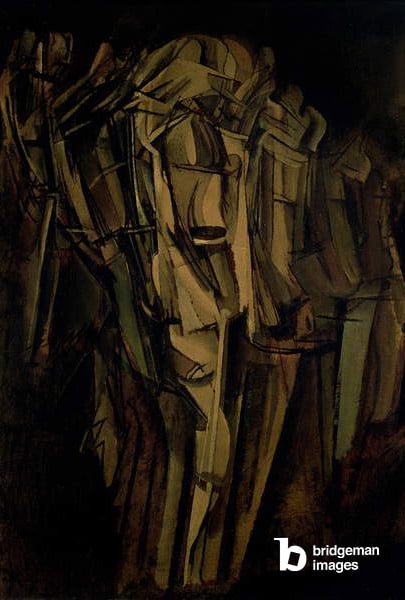

The 19th and 20th century Avant-Gardes make revolutionary changes to the nude: not only have we already seen a move away from the established academic tradition in art, the avant-gardes start to pull apart the very fabric of the body. Artists like Picasso famously fragmented the body into little pieces, while Egon Schiele represented it in a tortured way, the expressionists in Germany painted it in a rainbow of colours and surrealists switched body parts with objects.
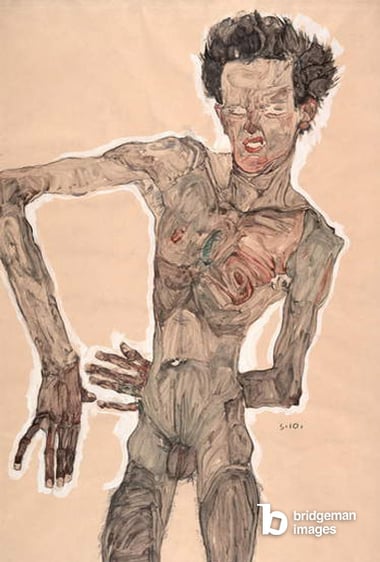
There are many more examples, and, perhaps for the first time, it becomes practically impossible to pinpoint a specific style of nude. What really unifies the male figure of this period is very much a mindset: the body’s boundaries and composition are not finite, and can be mixed up.

8) Man of the Masses
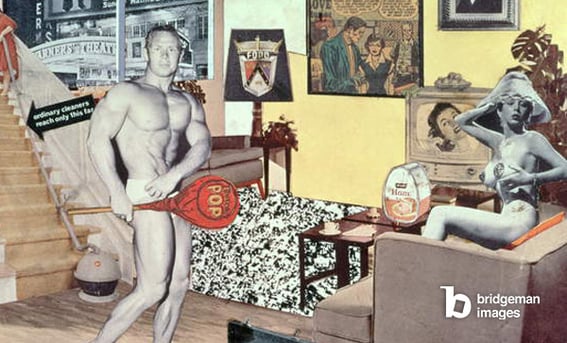
Later twentieth century male nudes is a category of extremes: it ranges anywhere between the extremely abstracted and expressive figures of Willem de Kooning to the mass-produced Pop-Art nude such as this one by Richard Hamilton.
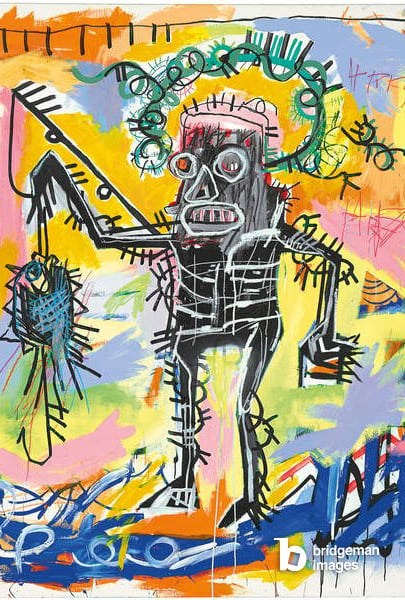

Mass culture greatly influences depictions of the body by Pop Artists, but this is not the only new cultural phenomenon that is reflected. Keith Haring and Basquiat later reference street art and culture with their style of painting the body.
9) Unsettling Man

From the later decades of the 20th century and to this day, we still haven’t stopped calling the body into question. The female body especially, and its potential to objectify and idealise, has been the topic of heated debate, but male nudity too has undergone changes in the past few decades.
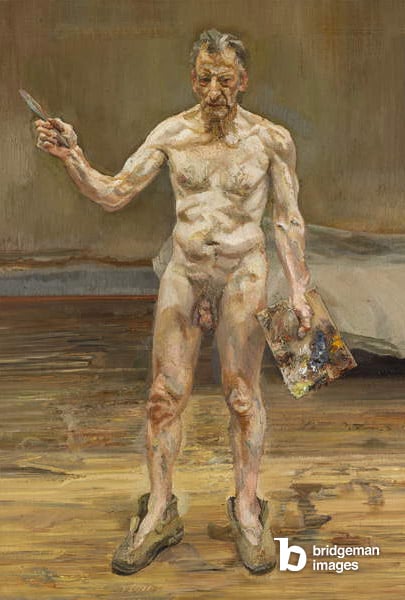

Again, there really isn’t a single type of nude to pinpoint, but artists now not only make changes to the body, but also draw attention to its more uncomfortable qualities and complexities. Artists like Lucian Freud for example show us a male body that is almost too real, too fleshy and unsettling for us to look at. Today’s body is confrontational, political and sometimes outright difficult to face. In other words, a world away from Classical Greece.

 Item added to cart
Item added to cart


